List of chromosomes » Chromosome 5
Gene… Where are you?
The human genome
Our chromosomes are made up of long molecules of DNA. If we were able to see a bit of DNA under the microscope, we would see that it is a simple succession of four different molecules: adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine, otherwise known as A, T, C and G.
The DNA of our 23 chromosomes has been sequenced. The result? 3 billions of A,T,C and G! It is what we call the human genome.

a gene?
Genes are bits of DNA of varied lengths. About 20’000 genes have been discovered, which produce all the proteins in our body. These genes are hidden inside a text which is 3 billion characters long. How do you find them? How do you read them? How do you make sense out of them?

from genes to proteins
All genes have a beginning and an end. Between the two limits lies a recipe which produces, for example, a protein. A protein is a succession of molecules known as amino acids, of which there are 20, all represented by a letter. Going from gene to protein is like going from Chinese to Russian. You need a translator. In other words, you need the genetic code.

One code for all
The genetic code is surprisingly simple.
3 consecutive ‘letters’ in DNA corresponds to 1 amino acid in a protein. By reading these three letter words, a DNA sequence is subsequently translated into a protein sequence. It is precisely in this way that our cells are able to produce proteins. And the genetic code is almost the same for all organisms: from viruses to elephants, bacteria to snails, and tulips to humans.

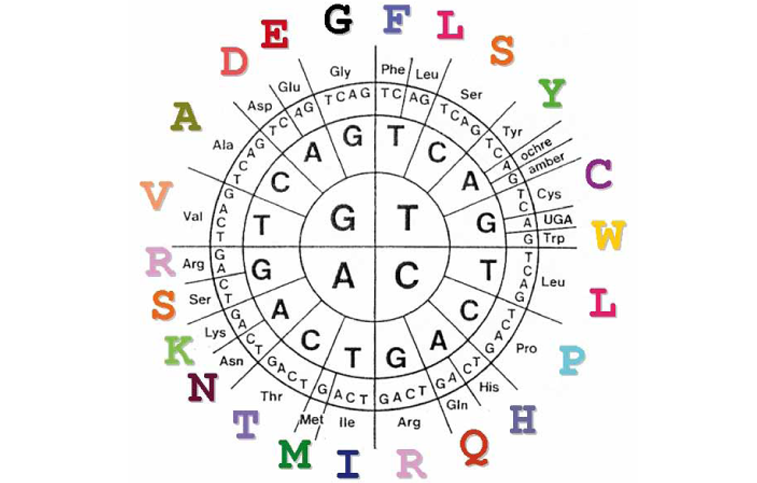
the genetic code
Here is one of the many ways of representing the genetic code. To read it:
start at the centre and move towards the outside.
An example: ATG (on the DNA) codes for amino acid M (methionine), and TTC codes for amino acid F (phenylalanine).
TAA, TAG and TGA do not code for an amino acid, but indicate a ‘stop’.

A needle in a haystack!
Nature is not simple. Genes which code for proteins represent less than 5% of our DNA. Finding them is like hunting for a needle in a haystack! What is more, not only are these genes scattered all over our DNA but they are also frequently in parts. Scientists then have to seek out the parts and reassemble them so that the gene can be read correctly.
Predicted genes
Computer programs were designed for just this problem and are able to predict the beginning of a gene, its end, and what is found between. Such programs are still light years away from giving perfect results, but they are a precious aid to biologists.

External links
Bioinformatics expert: Translate the DNA sequence ‘ggcgaaaacattgcgctg’ with the tool ‘Translate‘ (choose the ‘Output format’: Compact (“M”, “-“, no space) option)
Bioinformatics expert: Structure of the DROSHA gene (Ensembl database)
Corresponding protein in UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot
Bioinformatics expert: List of genes on chromosome 5
Internal links
What is a protein?
Protein Spotlight – comics: What’s a protein?