List of chromosomes » Chromosome 12
The story of life
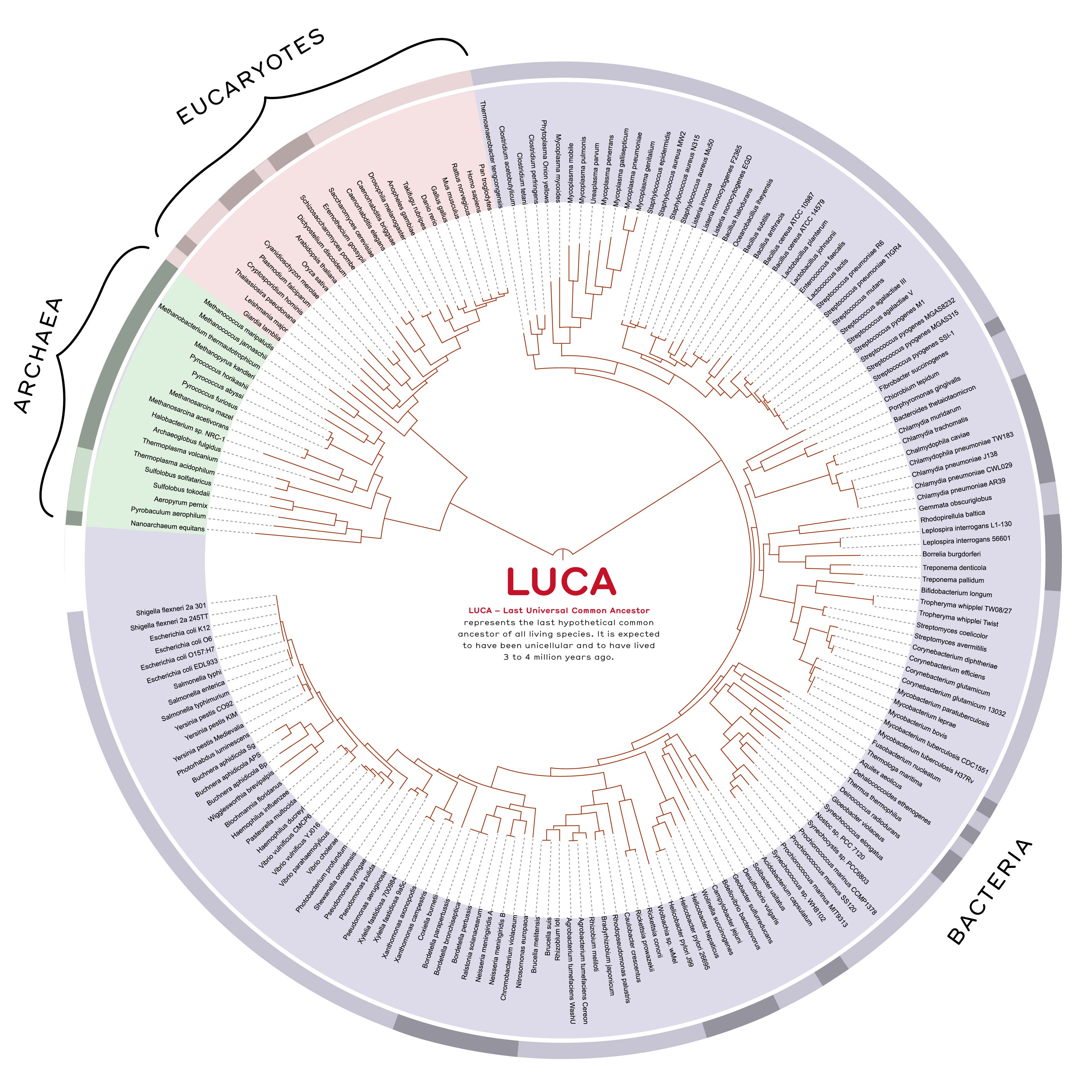
The tree of life
To define kinship, biologists look out for what is similar in species but also for what is dissimilar, in the same way you would examine a boy and his grandfather for instance. Echoing the family tree, biologists sum up the relationships between species in a tree: the tree of life.
In Darwin’s time, species were compared according to their morphology – the presence of fur or scales, the number of legs or, in plants, the position of leaves on a stalk for example.

Using the leap in knowledge made in the field of biology combined with the deciphering of the genomes of different species, it is currently possible to estimate the degree of parenthood between all species by ‘reading’ their genes and proteins. What is more, the calculating power of computers and high-performance bioinformatics methods of analysis are able to compare simultaneously a great number of genes, or proteins, between many species – from bacteria to humans.
Universal proteins
All species living on earth share something very intimate: ribosomes. The proteins that make up ribosomes are essential to life since they are themselves involved in making proteins. Ribosome proteins are frequently used by bioinformaticians to construct phylogenetic trees. There are about 200 other ‘universal’ proteins.

The tree of life
…created by scientists who compared 31 families of universal proteins from 191 different species.

The 3 domains of life
Bacteria / Eubacteria (Prokaryotes)
Unicellular organisms; their DNA is not kept inside a nucleus.
Archaea / (Prokaryotes)
Unicellular organisms; their DNA is not kept inside a nucleus. Unlike bacteria, however, archaea generally live in extreme conditions (high acidity, high temperatures, high pressure, …).
Eukaryotes
Organisms whose cells have a nucleus which protects their DNA. It is the case of animals – humans included – plants and fungi.
and
LUCA – Last Universal Common Ancester
represents the hypothetical last common ancestor of all living organisms. It is expected to have been unicellular and to have lived 3,5 to 4 billion years ago.